What is a roller coating?
 August 23, 2024
August 23, 2024 Hits:319second
Hits:319secondRoller Coating is a widely used industrial process where a liquid coating material is applied to a substrate (the material being coated) using a roller. This method is popular in various industries, including automotive, furniture, flooring, packaging, and electronics, due to its efficiency, precision, and consistency.

Key Components of Roller Coating:
Rollers:
Application Roller: Directly applies the coating to the substrate. Its surface can vary in texture and material, depending on the type of coating and the desired finish.
Doctor Roller: Helps to control the amount of coating applied by metering the excess material and ensuring even distribution.
Coating Material:
This can include paints, varnishes, adhesives, inks, or other specialized liquid coatings. The choice of material depends on the substrate and the end-use of the coated product.
Substrate:
The material being coated, such as metal, plastic, wood, paper, or fabric. The substrate is typically fed through the rollers at a controlled speed to ensure consistent application.
Types of Roller Coating Processes:
Direct Roller Coating:
In this method, the coating is applied directly to the substrate by the application roller. It is commonly used for flat surfaces.
Reverse Roller Coating:
Here, the rollers rotate in opposite directions, which allows for more precise control over the coating thickness and reduces the risk of streaking. This method is ideal for high-quality finishes.
Gap Coating:
A specific gap between the rollers determines the thickness of the applied coating. This is especially useful for achieving uniform layers.
Advantages of Roller Coating:
· Precision: Offers high control over the coating thickness and uniformity.
· Efficiency: Capable of coating large surfaces quickly and consistently.
· Versatility: Can be used with a wide range of coatings and substrates.
· Cost-Effective: Reduces material waste and can be automated for high-volume production.
Applications of Roller Coating:
· Automotive: Applying paints, primers, and finishes to car parts and panels.
· Furniture: Coating wood or veneer surfaces with stains, lacquers, or protective layers.
· Electronics: Coating circuit boards or other components with protective or conductive materials.
· Packaging: Coating paper or cardboard with adhesives, inks, or protective films.
Considerations in Roller Coating:
· Substrate Preparation: The substrate needs to be clean and free of contaminants to ensure good adhesion and a smooth finish.
· Coating Properties: The viscosity and drying time of the coating material must be suitable for the roller coating process.
· Equipment Maintenance: Rollers and other equipment must be regularly maintained to avoid defects and ensure consistent quality.
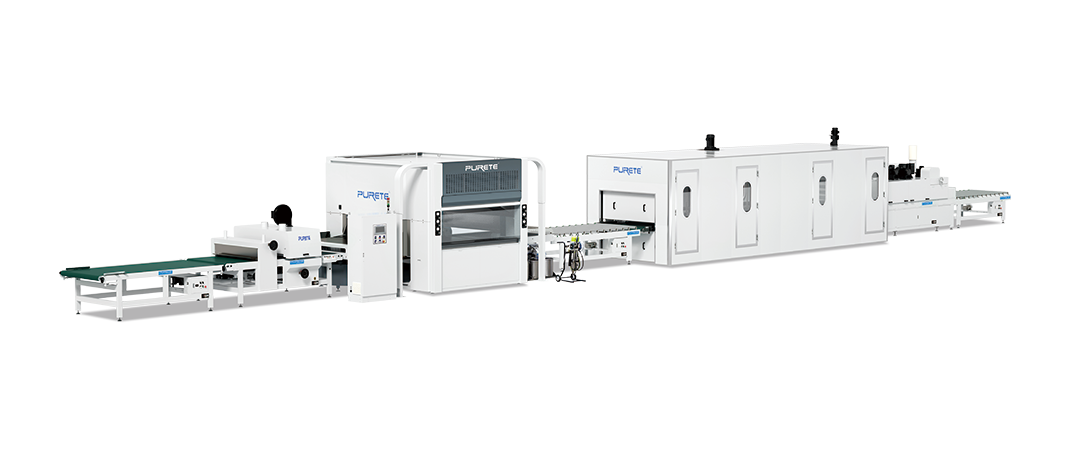
In summary, roller coating is a precise, efficient, and versatile method of applying liquid coatings to various substrates, making it a preferred choice in numerous industries. Building on these advantages, Purete's Roller Coating production line exemplifies the next generation of industrial coating processes.
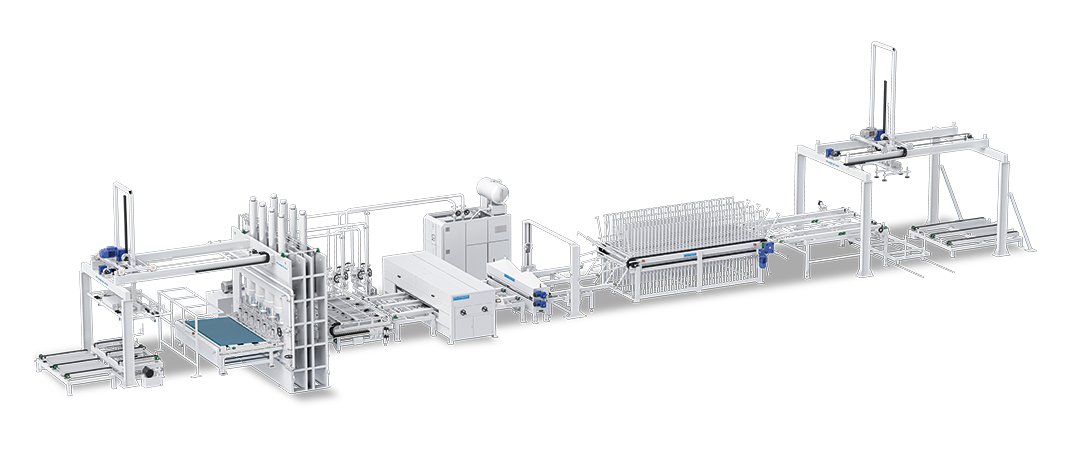
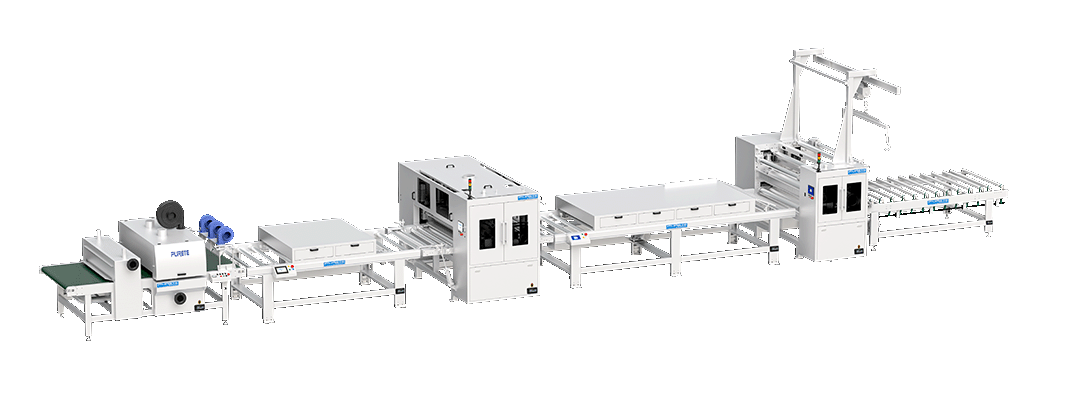
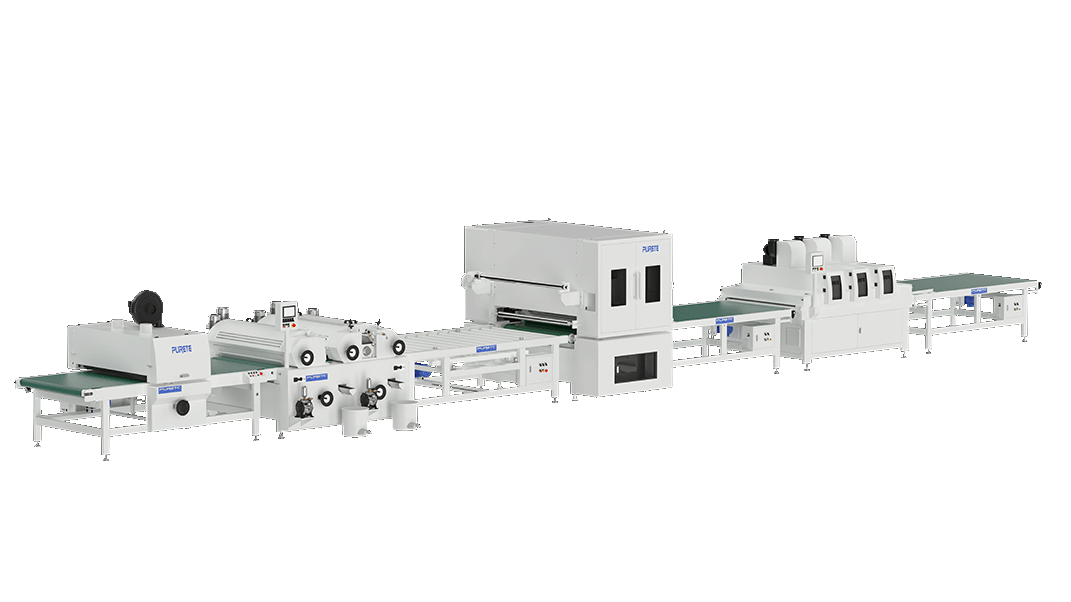
Purete offers an intelligent unmanned production system, which is specially designed for large panels. This system features fully automatic loading and unloading, integrated with intelligent control systems for a completely unmanned painting process. The production line is composed of several advanced components, including a loading machine, dust cleaner, filling and roller coating machine, three-lamp UV curing unit, and an unloading system. This cutting-edge technology not only enhances efficiency and precision but also ensures a high-quality finish, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications.